Significant progress all around
!function(e,t,n,s){var i=”InfogramEmbeds”,o=e.getElementsByTagName(t)[0],d=/^http:/.test(e.location)?”http:”:”https:”;if(/^\/{2}/.test(s)&&(s=d+s),window[i]&&window[i].initialized)window[i].process&&window[i].process();else if(!e.getElementById(n)){var a=e.createElement(t);a.async=1,a.id=n,a.src=s,o.parentNode.insertBefore(a,o)}}(document,”script”,”infogram-async”,”https://e.infogram.com/js/dist/embed-loader-min.js”);
Developments across Sub-Saharan Africa in 2017 exemplified the positive trend recorded globally, with Amnesty International’s research pointing to a further decrease in the global use of the death penalty in 2017.
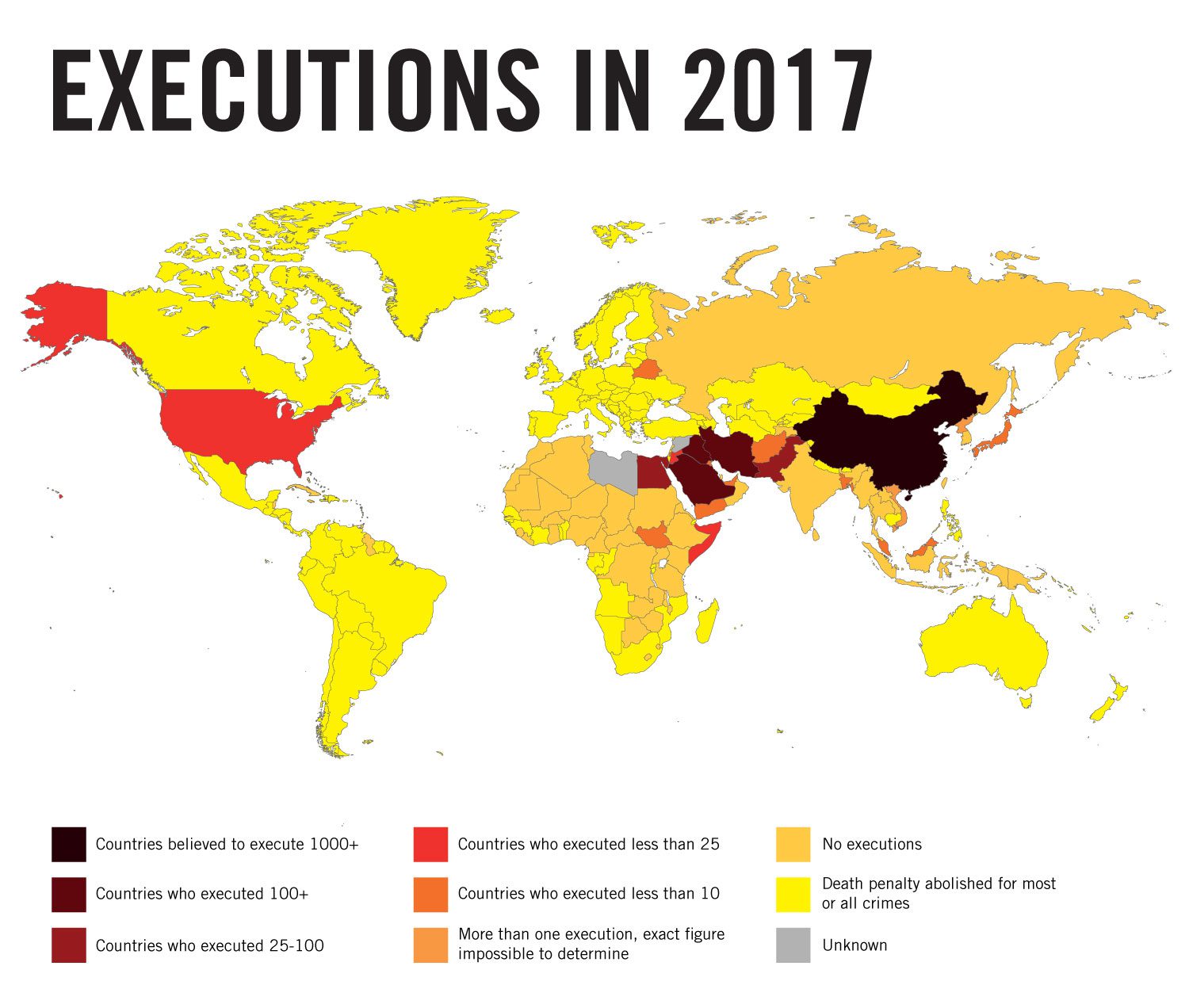
Amnesty International recorded at least 993 executions in 23 countries in 2017, down by 4% from 2016 (1,032 executions) and 39% from 2015 (when the organization reported 1,634 executions, the highest number since 1989). At least 2,591 death sentences in 53 countries were recorded in 2017, a significant decrease from the record-high of 3,117 recorded in 2016. These figures do not include the thousands of death sentences and executions that Amnesty International believes were imposed and implemented in China, where figures remain classified as a state secret.
In addition to Guinea, Mongolia abolished the death penalty for all crimes taking the total of abolitionist states to 106 in 2017. After Guatemala became abolitionist for ordinary crimes such as murder, the number of countries to have abolished the death penalty in law or practice now stands at 142. Only 23 countries continued to execute – the same number as in 2016, despite several states resuming executions after a hiatus.
Significant steps to reduce the use of the death penalty were also taken in countries that are staunch supporters of it. In Iran, recorded executions reduced by 11% and drug-related executions reduced to 40%. Moves were also made to increase the threshold of drug amounts required to impose a mandatory death penalty. In Malaysia, the anti-drug laws were amended, with the introduction of sentencing discretion in drug trafficking cases. These changes will likely result in a reduction in the number of death sentences imposed in both countries in the future.
“The fact that countries continue to resort to the death penalty for drug-related offences remains troubling. However, steps taken by Iran and Malaysia to amend their anti-drugs laws go a long way towards showing that cracks are appearing, even in the minority of countries that still execute people,” said Salil Shetty.
Download the report HERE: P4975 DP_Report_2017